Check if a given array can represent Preorder Traversal of Binary Search Tree
A Simple Solution is to do following for every node pre[i] starting from first one.
1) Find the first greater value on right side of current node.
Let the index of this node be j. Return true if following
conditions hold. Else return false
(i) All values after the above found greater value are
greater than current node.
(ii) Recursive calls for the subarrays pre[i+1..j-1] and
pre[j+1..n-1] also return true.
Time Complexity of the above solution is O(n2)
bool canRepresentBST_v2(int arr[], int start, int end){
if (start >= end)
return true;
int curNode = start++;
while (start < end) {
if (arr[curNode] < arr[start]) {
for (int k = start + 1; k < end; ++k) {
if (arr[curNode] > arr[k])
return false;
}
return (canRepresentBST_v2(arr, curNode + 1, start) && canRepresentBST_v2(arr, start + 1, end));
}
start++;
}
return true;
}
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
For every element Preorder[i], i=0 to n. Find the first greater value(start of Right sub-tree) than current node. Let the index at which first greater element found be j.
Return True if following conditions satisfies else return False,
1. All values after the above found greater element are greater than current node.
2. Recursively calls for the sub-arrays Preorder[ i+1 ... j-1 ] and Preorder[ j+1 ... n-1 ],
So that all elements are covered and return true if they also satisfies point 1.
This method requires O(N^2) time complexity to check Preorder sequence is valid or not.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| public class VerifyPreorderSequenceInBinarySearchTree { public static void main(String[] args) { new VerifyPreorderSequenceInBinarySearchTree(); } public VerifyPreorderSequenceInBinarySearchTree() { int[] preOrderTraversal = {30, 20, 10, 40, 50}; System.out.println(isValid(preOrderTraversal, 0, preOrderTraversal.length-1, Integer.MIN_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE)); } public static boolean isValid(int arr[], int start, int end, int min, int max){ if(start>=end){ return true; } int root = arr[start]; //Find Max index int maxIndex = start; for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) { if(arr[i] < min || arr[i] > max){ return false; } if(arr[i] > root){ break; } maxIndex++; } boolean left = isValid(arr, start+1, maxIndex-1, min, arr[start]-1); //arr[start]-1 because for next recursive call, max should be one less(on Left side) as we are assuming BST doesn't contain duplicates boolean right = isValid(arr, maxIndex, end, arr[start]+1, max); //arr[start]+1 because for next recursive call, min should be one more(on Right side) as we are assuming BST doesn't contain duplicates return left && right; }} |
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
In this approach, we will use 2 Stacks.
Stack 1 will hold Preorder values. It means stack will grow in ascending order.
Bottom of the stack will have largest value and on top will be smallest.
Stack 2 will hold Inorder values. It means stack will grow in descending order.
Bottom of the stack will have smallest value and on top will be largest.
We will start reading given Preorder traversal from i=0 to n.
We already saw that Root Node will be first in Preorder traversal followed by Left sub-tree elements followed by Right sub-tree elements.
So if the given Preorder traversal is a valid traversal sequence of BST then you will encounter
1. Highest element first, followed by
2. All smaller elements(Left sub-tree) compared to first element, followed by
3. All higher elements(Right sub-tree) compared to first element.
We will validate the given Preorder traversal is a valid traversal sequence of BST by using above 2 stacks.
Start reading given Preorder traversal and put elements into Stack 1.
While putting elements to Stack 1, make sure that element at top of the stack is larger that current element i.
As soon as you encounter current element i is greater than element at top of stack, Stop here and
start popping the element from stack until you find the elements greater than current element i and put the current element i on top of Stack 1.
Push the poped elements from Stack 1 to Stack 2 which is holding values in Inorder fashion.
(Stack 2 will always have element at top higher than below elements.)
As soon as you find that element pushed to Stack 2 is smaller than the element present on top of Stack 2. Stop here, because this happens only when given Preorder traversal is INVALID traversal sequence of BST otherwise pushed element from Stack 1 will always be the greater element than element present on top of Stack 2.
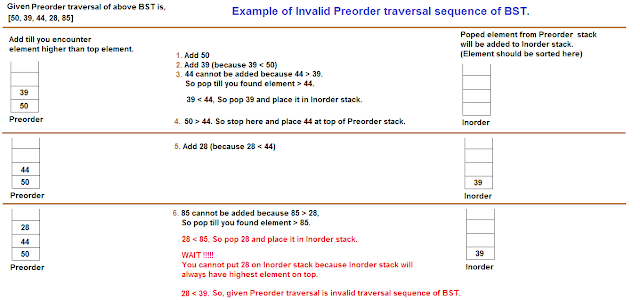
Lets understand it with the help of both Valid and Invalid scenario example.
Valid example.
Invalid Example.
Inorder stack(Stack 2) that we used for storing values is no where used in the program except the element at the top of the stack which is used to compare it with the new element to be placed on top of it.
So instead of taking stack we can use some variable say "topElementAtInorderStack", that will hold the value at the top of Inorder stack and we will compare the value to be placed on top of the stack with this variable.
If the value to be placed on top of Stack 2 is LARGER than variable topElementAtInorderStack, then we will update topElementAtInorderStack to hold new value.
If the value to be placed on top of Stack 2 is SMALLER than variable topElementAtInorderStack, then we will Stop our execution because it says that given Preorder traversal is INVALID traversal sequence of BST.
Stack 1 will hold Preorder values. It means stack will grow in ascending order.
Bottom of the stack will have largest value and on top will be smallest.
Stack 2 will hold Inorder values. It means stack will grow in descending order.
Bottom of the stack will have smallest value and on top will be largest.
We will start reading given Preorder traversal from i=0 to n.
We already saw that Root Node will be first in Preorder traversal followed by Left sub-tree elements followed by Right sub-tree elements.
So if the given Preorder traversal is a valid traversal sequence of BST then you will encounter
1. Highest element first, followed by
2. All smaller elements(Left sub-tree) compared to first element, followed by
3. All higher elements(Right sub-tree) compared to first element.
We will validate the given Preorder traversal is a valid traversal sequence of BST by using above 2 stacks.
Start reading given Preorder traversal and put elements into Stack 1.
While putting elements to Stack 1, make sure that element at top of the stack is larger that current element i.
As soon as you encounter current element i is greater than element at top of stack, Stop here and
start popping the element from stack until you find the elements greater than current element i and put the current element i on top of Stack 1.
Push the poped elements from Stack 1 to Stack 2 which is holding values in Inorder fashion.
(Stack 2 will always have element at top higher than below elements.)
As soon as you find that element pushed to Stack 2 is smaller than the element present on top of Stack 2. Stop here, because this happens only when given Preorder traversal is INVALID traversal sequence of BST otherwise pushed element from Stack 1 will always be the greater element than element present on top of Stack 2.
Lets understand it with the help of both Valid and Invalid scenario example.
Valid example.
Invalid Example.
In this approach we will try to save the extra memory we used in Approach 3.
Inorder stack(Stack 2) that we used for storing values is no where used in the program except the element at the top of the stack which is used to compare it with the new element to be placed on top of it.
So instead of taking stack we can use some variable say "topElementAtInorderStack", that will hold the value at the top of Inorder stack and we will compare the value to be placed on top of the stack with this variable.
If the value to be placed on top of Stack 2 is LARGER than variable topElementAtInorderStack, then we will update topElementAtInorderStack to hold new value.
If the value to be placed on top of Stack 2 is SMALLER than variable topElementAtInorderStack, then we will Stop our execution because it says that given Preorder traversal is INVALID traversal sequence of BST.
Java Program to check if a given array can represent Preorder Traversal of Binary Search Tree
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
| package tree;import java.util.Stack;public class VerifyPreorderSequenceInBinarySearchTree { public static void main(String[] args) { new VerifyPreorderSequenceInBinarySearchTree(); } public VerifyPreorderSequenceInBinarySearchTree() { int[] preOrderTraversal = {40, 30, 35, 20, 80, 100}; boolean flag = checkPreorderCanRepresentBST(preOrderTraversal); if(flag){ System.out.println("Valid Preorder traversal"); }else{ System.out.println("Invalid Preorder traversal"); } } private static boolean checkPreorderCanRepresentBST(int[] preOrderTraversal){ //Stack for holding elements in Preorder fashion. Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>(); //Instead of Stack, we are taking variable which will hold last value at top of Inorder stack. //initializing it to Integer.MIN_VALUE, So that next value should be greater than this atleast. int lastInOrderNumber = Integer.MIN_VALUE; for (int i=0; i<preOrderTraversal.length; i++) { int data = preOrderTraversal[i]; //If any value we encounter which is less than already stored last value in Inorder stack(lastInOrderNumber), return false. //If the value coming in is less it means preorder is not valid otherwise it will always be in increasing order. if(data < lastInOrderNumber){ return false; } //If the Preorder stack peek contains element which is smaller than current working data, //then pop till you find element greater than current working data. //also mark last poped data as lastInOrderNumber. while(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() < data ){ lastInOrderNumber = stack.peek(); stack.pop(); } stack.add(data); } return true; }} |



No comments:
Post a Comment